| Main | Births etc |
|---|
| St Tudy | |
| Cornish: Eglostudi | |
 St Tudy |
|
| OS grid reference | |
|---|---|
| Unitary authority | Cornwall |
| Ceremonial county | Cornwall |
| Region | South West |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | BODMIN |
| Postcode district | PL30 |
| Dialling code | 01208 |
| Police | Devon and Cornwall |
| Fire | Cornwall |
| Ambulance | South Western |
| EU Parliament | South West England |
| UK Parliament | North Cornwall |
| List of places: UK • England • Cornwall | |
St Tudy (Cornish: Eglostudi) is a civil parish and village in north Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The village is situated in the River Camel valley approximately five miles northeast of Wadebridge.[1]
The village is mentioned as having a cattle fair in Owen's book of fairs 1788.[2]
Notable houses[]
There was formerly a manor house at Tinten and the chapel may still be recognized. It has been reused as a barn and has a 15th-century window.[3] Other small former manor houses in the parish are Hengar, which was destroyed by a fire in 1904 (in 1906 it was rebuilt in Elizabethan style); Lamellen, Tremeer and Wetherham[4] One of the most well-known of Thomas Rowlandson's paintings is "Hengar House the seat of Matthw Mitchell [sic] Esqr., Cornwall" (1812) which was sold at the Sir Richard Onslow sale, Sotheby's, 15 July 1959. Hengar was a country seat of the Onslows.[5]
Parish church[]

St Tudy Church and War Memorial
The parish church is dedicated to St Tudius and was restored in 1873. There was a Norman church here but the present structure is of the Perpendicular period. There are two aisles the arcades of which are identical.[6] The tower has three stages, is 64 feet high, and is topped with battlements and pinnacles; there are five bells.[7] It is Grade I listed.[8] Anthony Nicholl (died 1658) is commemorated by a sumptuous memorial erected by his wife.[9] In the churchyard is a pre-Norman coped stone with carving, possibly a rare hogback tomb. [10][11]
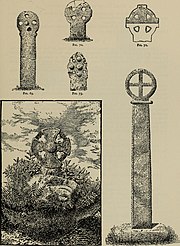
Trevenning cross (fig. 70) illustrated in The Victoria History of the County of Cornwall (1906)
Trevenning cross is at a road junction about one and a half miles northeast of the churchtown. It was found in the hedge close to its present position by J. R. Collins of Bodmin.[12]
Notable people[]
Notable people from St Tudy include: William Bligh, naval officer; Eddie George, former governor of the Bank of England; Oscar Kempthorne, statistician and geneticist at Iowa State University; Richard Lower, early experimenter in blood transfusion; Humphrey Nicholls, MP for Bodmin; and Vice Admiral Sir Louis Le Bailly who led a campaign for the local pub to be renamed after William Bligh.[13]
References[]
- ^ Ordnance Survey: Landranger map sheet 200 Newquay & Bodmin ISBN 978-0-319-22938-5
- ^ "Owen's New Book of Fairs: Published by the King's Authority. Being a ... : William Owen : Free Download & Streaming : Internet Archive". archive.org. 2014. https://archive.org/details/owensnewbookfai00owengoog. Retrieved 2 August 2014.
- ^ Pevsner, N. (1970) Cornwall; 2nd ed., revised by Enid Radcliffe. Harmondsworth: Penguin; p. 221
- ^ Beacham, Peter & Pevsner, Nikolaus (2014) Cornwall.(The Buildings of England.) New Haven: Yale University Press; p. 605
- ^ "Sir William and Lady Onslow". The Cornishman (66): p. 6. 16 October 1879.
- ^ Pevsner, N. (1970) Cornwall; 2nd ed. Penguin Books; p. 203
- ^ "St Tudy". Genuki.org.uk. 2012-03-25. http://www.genuki.org.uk/big/eng/Cornwall/StTudy/. Retrieved 2015-06-26.
- ^ Details from listed building database (67804) . Images of England. English Heritage., accessed 28 March 2010
- ^ [1] Archived September 29, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "myADS". Archaeology Data Service. http://archaeologydataservice.ac.uk/archiveDS/archiveDownload?t=arch-721-1/dissemination/pdf/southwes1-131402_1.pdf. Retrieved 2015-10-23.
- ^ Pevsner (1970)
- ^ Langdon, A. G. (1896) Old Cornish Crosses. Truro: Joseph Pollard; p. 184
- ^ "Vice-Admiral Sir Louis Le Bailly - Telegraph". The Daily Telegraph (London: TMG). ISSN 0307-1235. OCLC 49632006. http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/obituaries/military-obituaries/naval-obituaries/8084056/Vice-Admiral-Sir-Louis-Le-Bailly.html. Retrieved 4 December 2014.
External links[]
Media related to St Tudy at Wikimedia Commons
| |||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| This page uses content from the English language Wikipedia. The original content was at St Tudy. The list of authors can be seen in the page history. As with this Familypedia wiki, the content of Wikipedia is available under the Creative Commons License. |